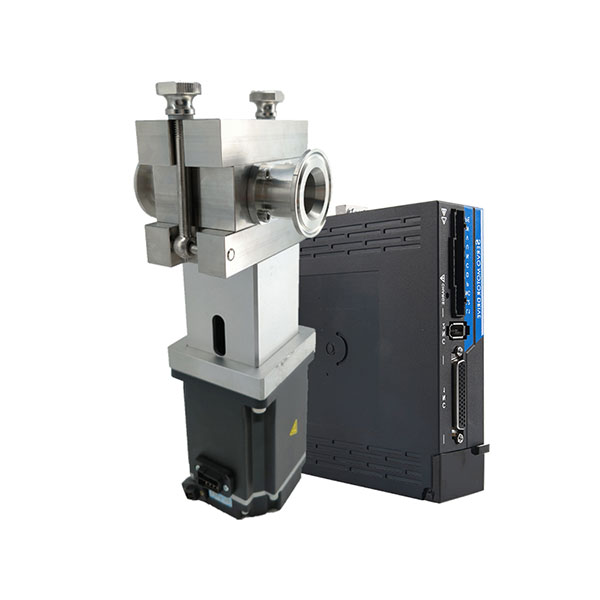
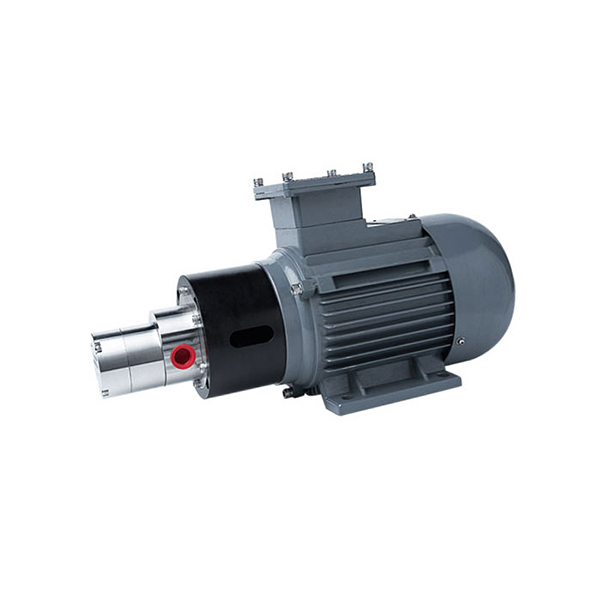
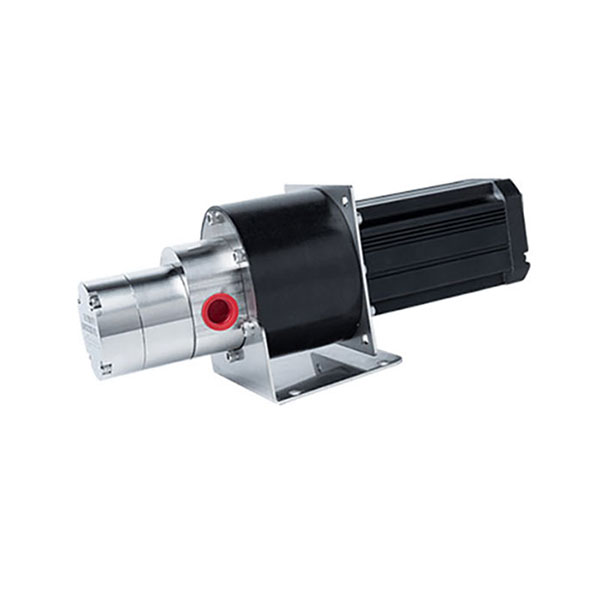
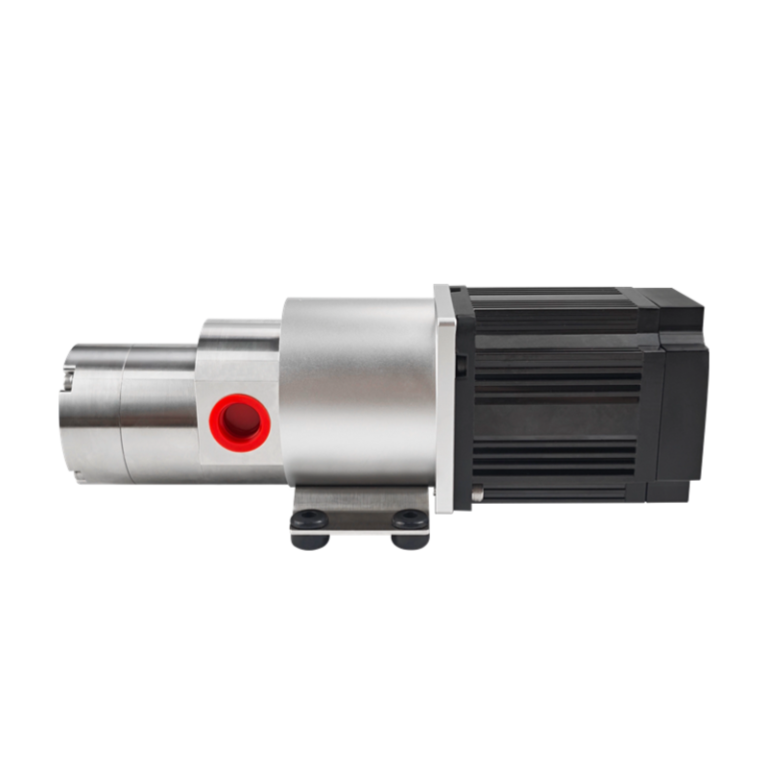
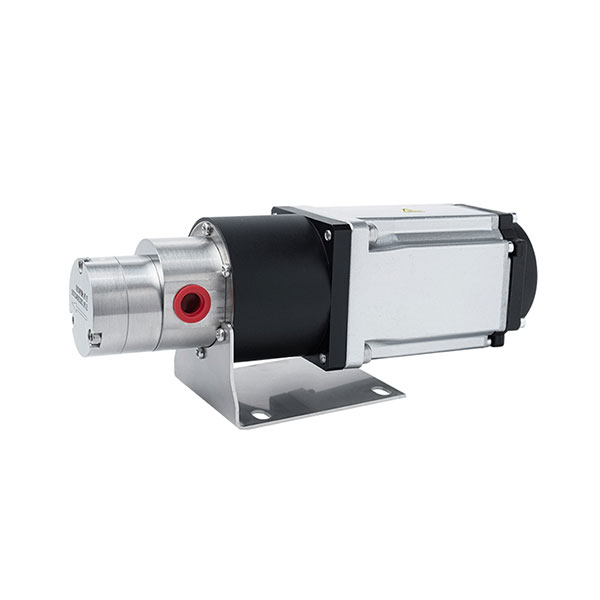
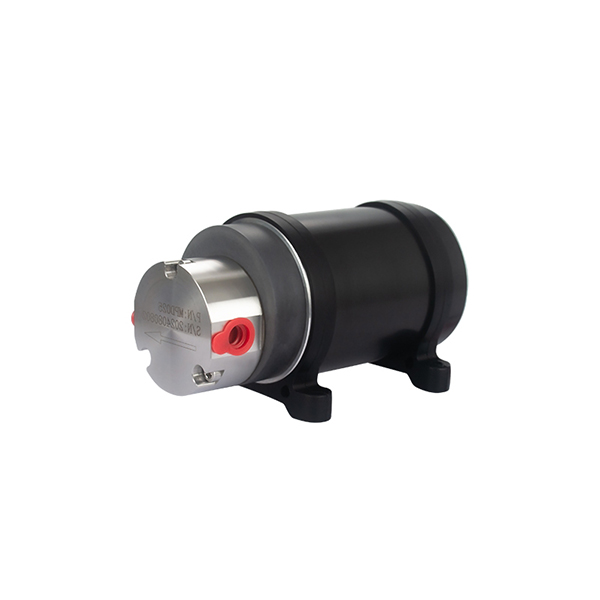
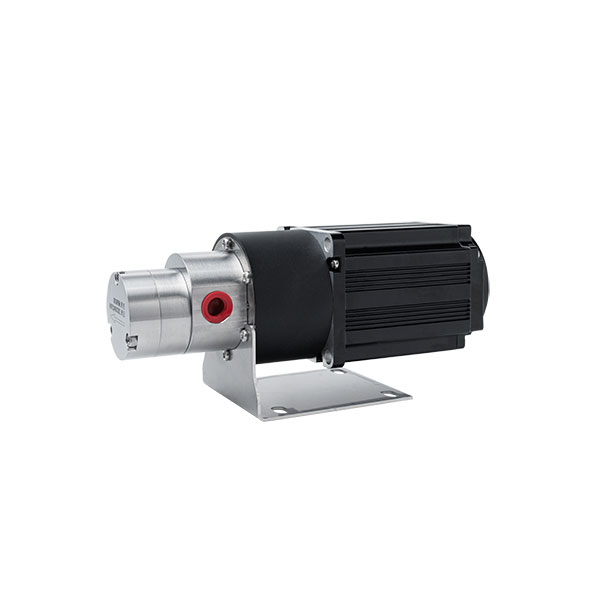
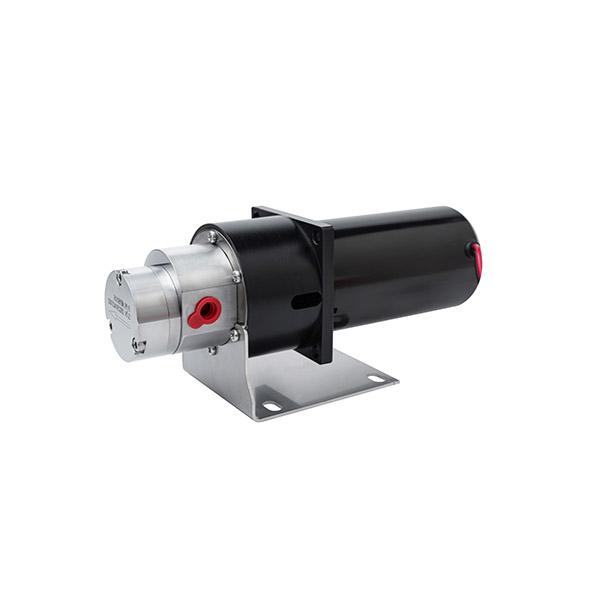
Micro External Gear Pumps
CHENHUI design and manufacture high-quality micro pumps for precise fluid handling in various industries. Our pumps feature an external gear design, which enhances performance and ensures durability, even in demanding applications. The magnetic drive technology ensures leak-free operation and reduces maintenance needs. Our micro gear pumps offer long-lasting, efficient solutions for applications requiring small-volume, low flow and high-precision fluid transfer.
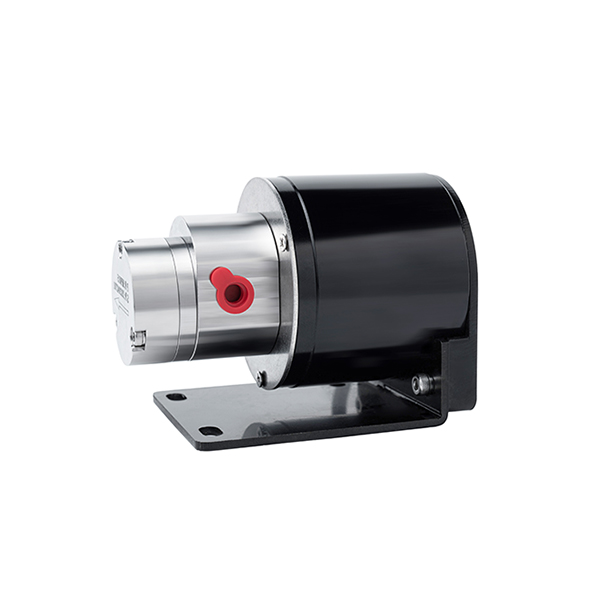
External Gear MIcro Pump Series
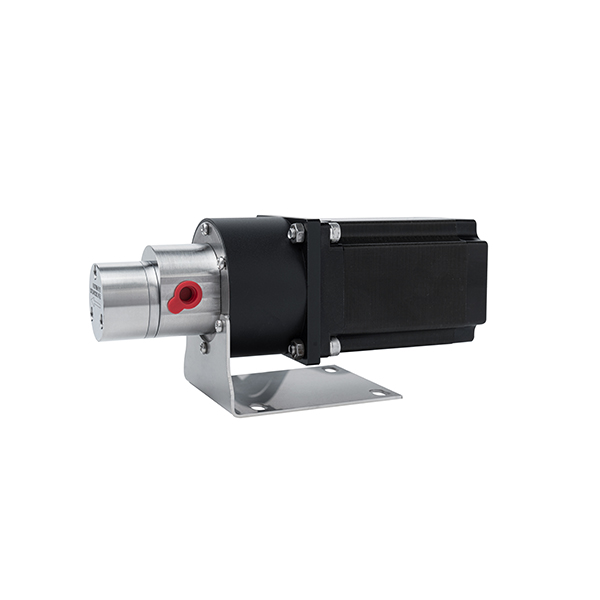
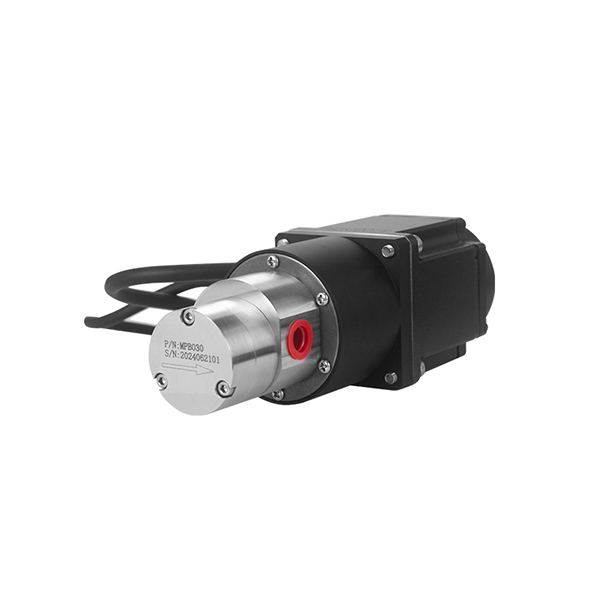
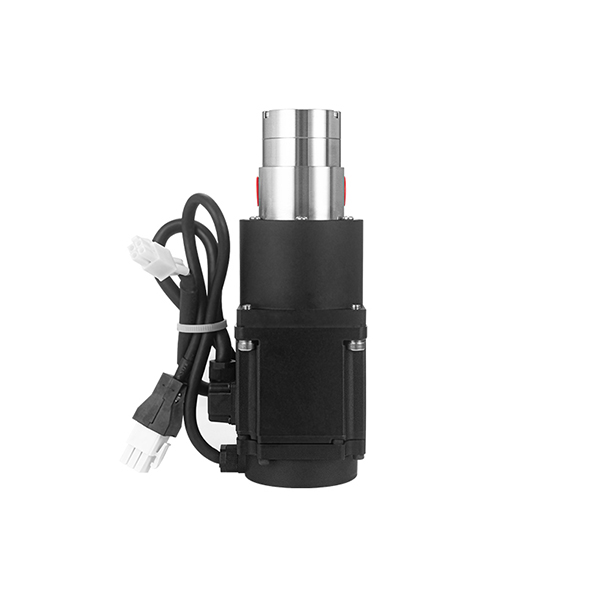
Magnetic Drive Pump + Motor Series
What is External Gear Pump?
An external gear pump is a type of positive displacement pump widely used in industrial applications for precise fluid transfer. It operates with two identical gears that rotate in opposite directions inside a sealed casing. As the gears mesh, they create cavities that draw fluid into the pump inlet, carry it around the casing, and then force it out through the discharge port.
External gear pumps deliver a consistent, smooth flow directly proportional to the gear rotation speed, making them ideal for metering and lubrication systems where precise fluid control is crucial.
Advantages of External Gear Pumps:
- High Pressure Capability
With tight internal clearances and dual shaft bearings, external gear pumps are designed to handle high-pressure applications efficiently. Durable and Reliable
Their robust mechanical design supports long service life when used with clean, non-abrasive fluids such as oils, fuels, and chemical additives.Smooth, Pulse-Free Flow
The meshing gears produce a consistent, low-pulsation flow, ensuring stable and accurate fluid delivery.Easy Maintenance
The simple internal structure allows for quick disassembly and servicing, minimizing downtime and reducing overall maintenance costs.Self-Priming Capability
As a positive displacement pump, it offers strong self-priming performance, enabling reliable fluid intake even when the suction line is initially dry—crucial during system start-up.
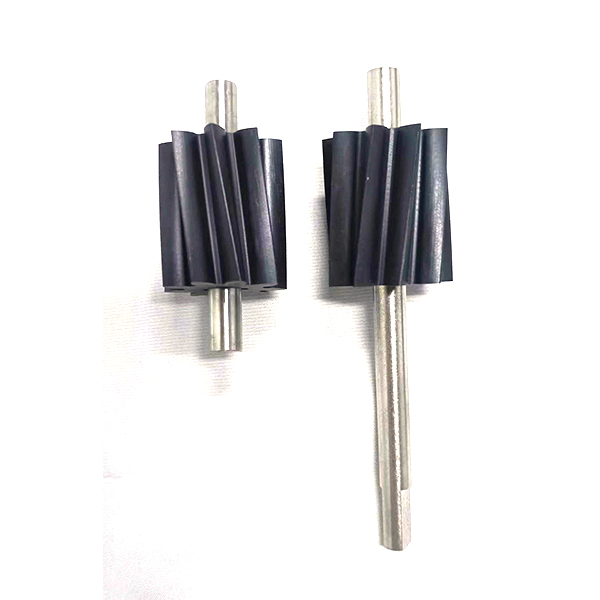

How Does an External Gear Pump Work?
An external gear pump operates using two intermeshing gears—typically one drive gear and one idler gear—mounted inside a tightly machined housing. As the motor turns the drive gear, it simultaneously rotates the idler gear in the opposite direction.
Inlet (Filling)
As the gears rotate and come out of mesh on the inlet side, cavities form between the gear teeth and the pump casing. This creates a vacuum that draws fluid into the pump.
Transfer (Transport)
The fluid is trapped in the pockets between the gear teeth and the casing. These pockets carry the fluid around the outside of the gears toward the outlet side. Importantly, no fluid passes between the gears, since they are always tightly meshed in the center.
Outlet (Discharge)
On the outlet side, the gears come back into mesh, reducing the volume between the teeth and forcing the fluid out under pressure through the discharge port.
CHENHUI pump's Magnetic Drive Mechanism
Our micro external gear pumps feature magnetic coupling that connects the motor to the pump gears without direct contact. When the motor starts, it drives magnets that, through magnetic forces, rotate the pump’s gears. This design eliminates shaft seals, preventing leaks and reducing maintenance while ensuring smooth, reliable fluid transfer.


Materials of Construction
Our micro external gear pumps can be constructed from a wide range of materials. By precisely matching the pump materials to the liquid being handled, they offer superior service life—even when pumping highly corrosive or aggressive fluids.
Peek Gear
PEEK stands out for its excellent chemical resistance, strong mechanical properties, and ability to withstand high temperatures. This ensures the gears operate smoothly under continuous stress and in contact with aggressive fluids
316 Stainless Steel Body
The pump casing is made of 316 stainless steel, a material widely recognized for its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. This ensures the pump housing can withstand harsh industrial environments and aggressive fluids without compromising structural integrity or safety.
Shaft Material Options
To meet different industrial requirements, Chenhui offers shafts in four material variants:
- 316L Stainless Steel: Known for its corrosion resistance and strength, this material suits general chemical and industrial fluids, balancing durability and cost-effectiveness.
- Ceramic: Ideal for highly corrosive or abrasive liquids, ceramic shafts resist wear and chemical attack, ensuring pump reliability in harsh conditions.
- Tungsten Steel: Offering superior wear resistance and toughness, tungsten steel shafts are perfect for demanding applications involving abrasive particles or high mechanical loads.
- Titanium Alloy: Lightweight and extremely corrosion-resistant, titanium alloy shafts are designed for environments where weight savings and maximum chemical resistance are critical.
Shaft Seal Area
Rubber O-Rings: Suitable for standard fluid sealing requirements, offering flexibility and durability in moderate chemical environments.
PTFE Gaskets: For more aggressive or corrosive fluids, PTFE gaskets provide superior chemical resistance and temperature tolerance, protecting the pump internals and extending maintenance intervals.
Why Choose CHENHUI For High Quality External Gear Pumps
1. Long Service Life
Durability begins with design. A properly engineered gear pump should feature optimized bearing sizes and wear-resistant materials. These elements reduce internal friction and extend operating life. Fluid type, pressure, and temperature also affect lifespan. When the pump is matched correctly to the application, it can operate reliably for years with minimal maintenance.
2. Leak-Free Operation
Conventional gear pumps often rely on shaft seals, which are prone to wear and leakage. A better solution is magnetic coupling. This design eliminates the need for dynamic seals, minimizing failure points and ensuring safe, leak-free performance—especially in systems that handle corrosive or sensitive fluids.
3. Stable Low Flow Output
Micro gear pumps are often used in applications that require accurate dosing or consistent circulation at low flow rates. Tight machining tolerances and precision assembly ensure repeatable, pulse-free output, even at low speeds. This makes the pump ideal for metering, sampling, or small-scale transfer systems.
4. High Differential Pressure Capability
A robust gear set and precision housing allow high differential pressures without compromising flow stability. This is critical for systems with high resistance or back pressure. A quality micro gear pump should maintain performance even at pressure differentials up to 25 bar, depending on the configuration.
5. Customization Support
Not all applications are the same. Leading manufacturers provide customization options—such as alternative materials, port configurations, motor types, and flow rates—to meet specific system requirements. Tailored solutions improve performance, compatibility, and overall system efficiency.
Frequent Asked Questions
Are External Gear Pumps Fixed Displacement?
Yes, external gear pumps are fixed displacement pumps. This means that they deliver a consistent volume of fluid with each rotation of the gears. The displacement per cycle remains constant, which makes these pumps reliable for applications requiring a steady flow of fluid.
Are External Gear Pumps Reversible?
External gear pumps are generally not reversible. They are designed to pump fluid in a specific direction. If you want to reverse the flow direction, you might need to require adjustments to the pump’s configuration.
Can External Gear Pumps Move Fluid in Either Direction?
Most external gear pumps are built to deliver fluid in one specific direction, and attempting to reverse the flow without proper modification could damage the pump or lead to inefficiency.
What Causes Discharge of Fluid in an External Gear Pump?
The discharge of fluid in an external gear pump is caused by the meshing of the two rotating gears. As the gears turn, they create a void or suction, drawing fluid into the pump. The meshing teeth then force the fluid into the discharge port, effectively displacing it.