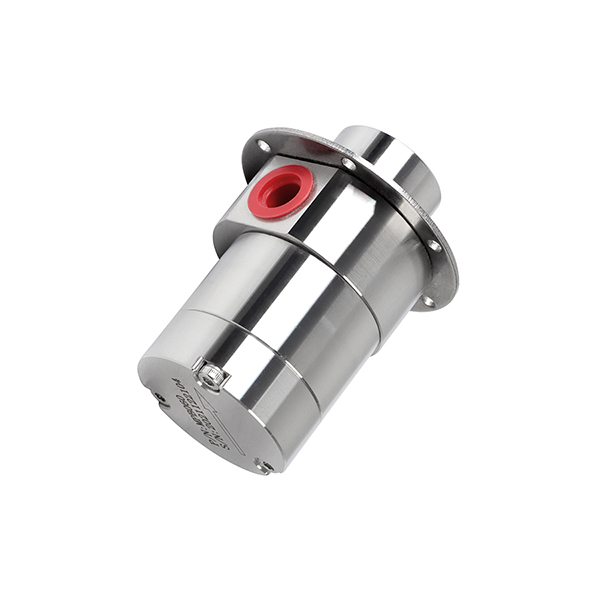
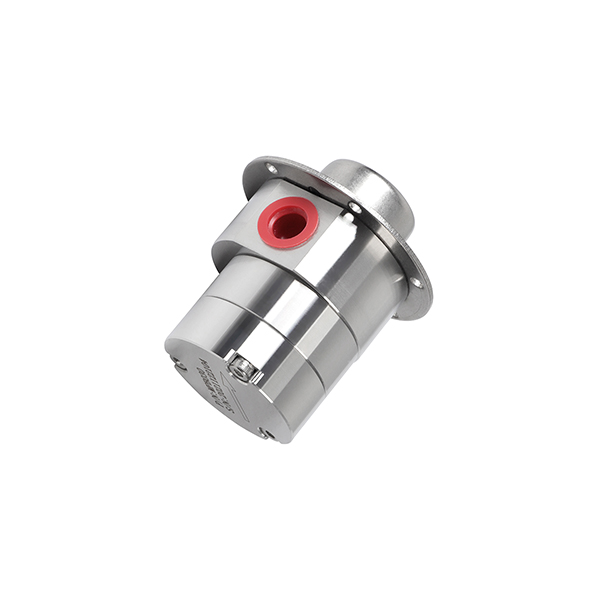
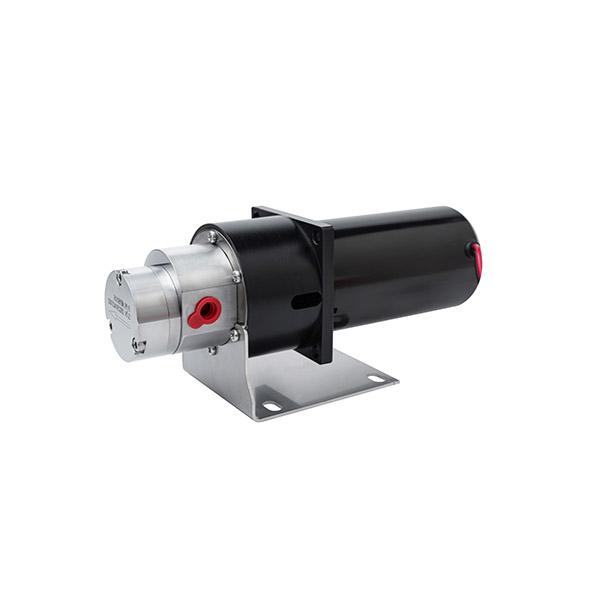
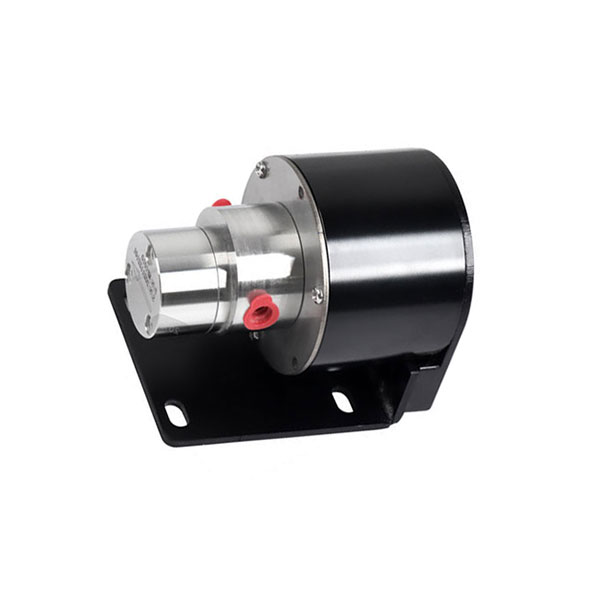
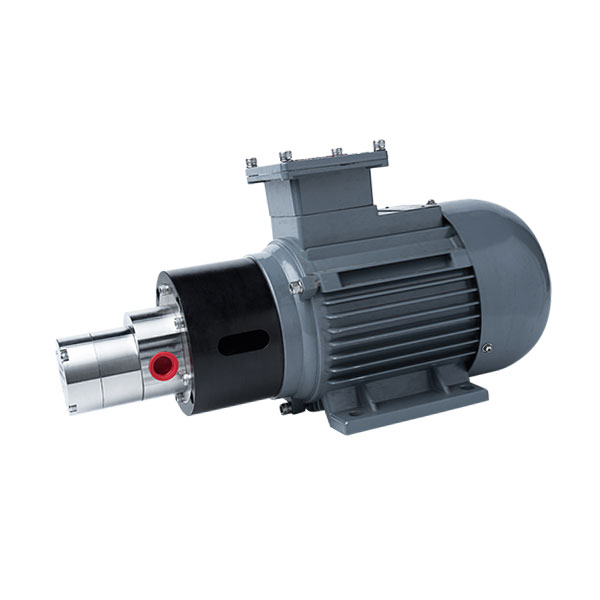
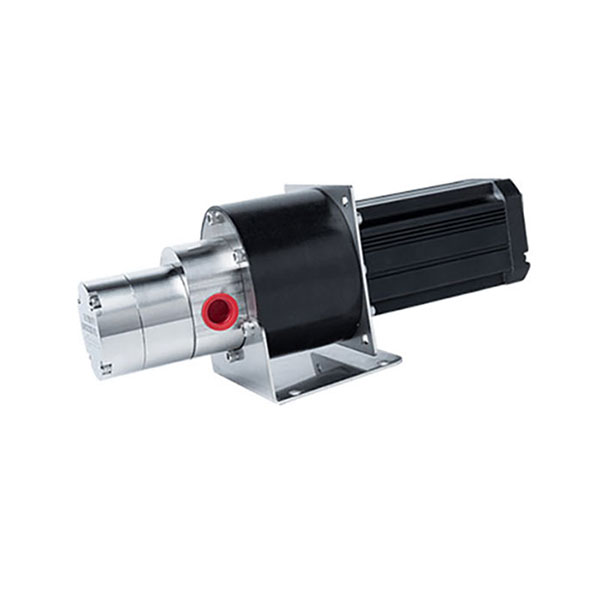
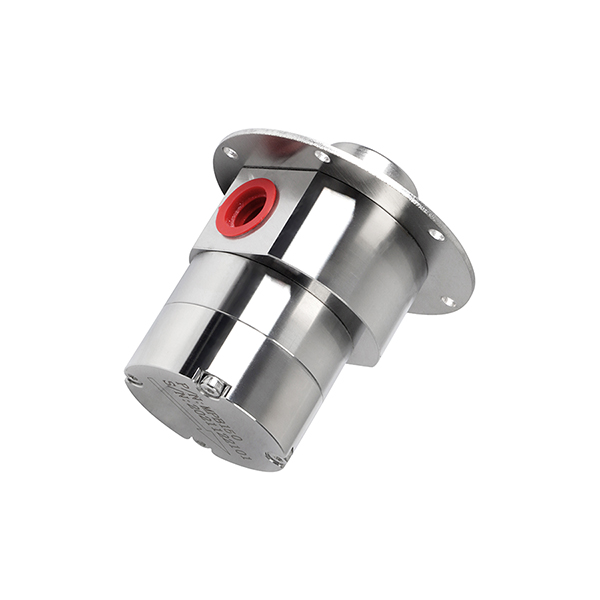
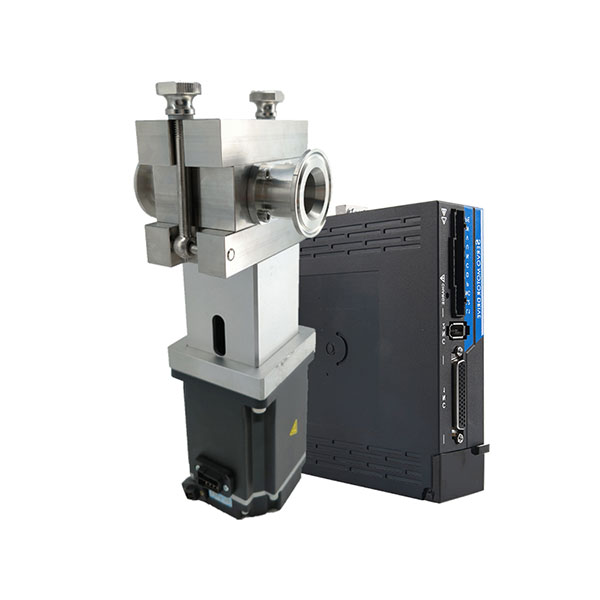
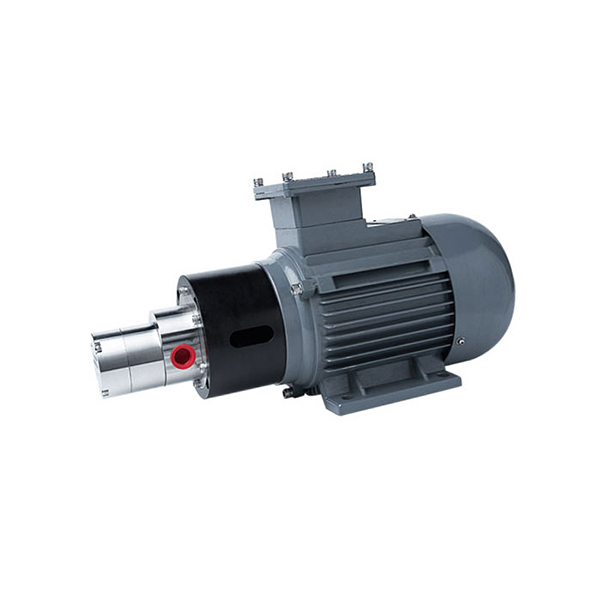
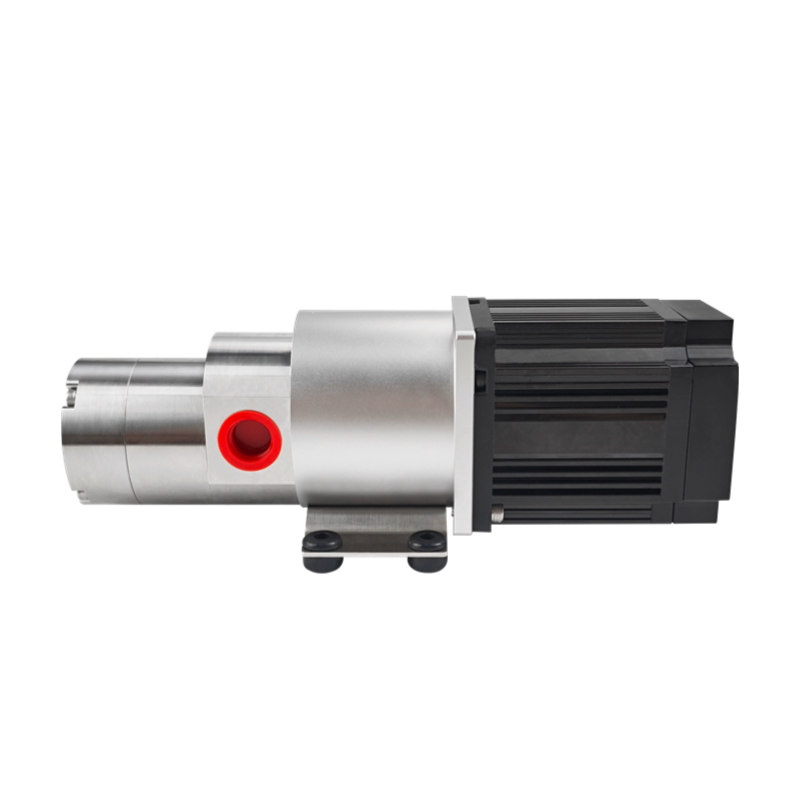
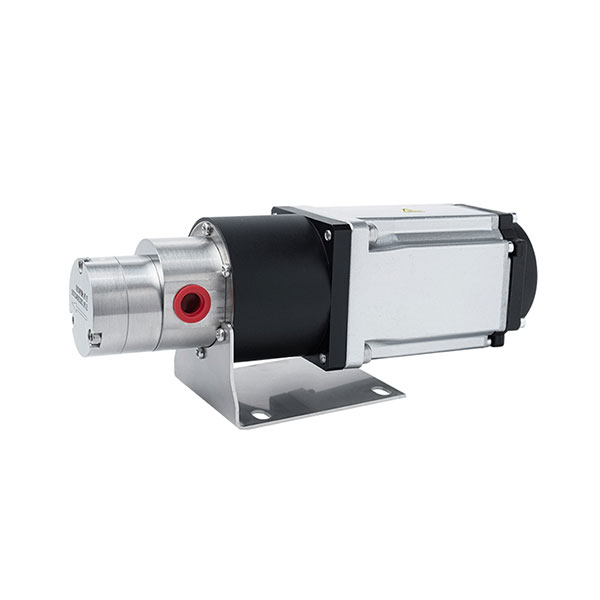
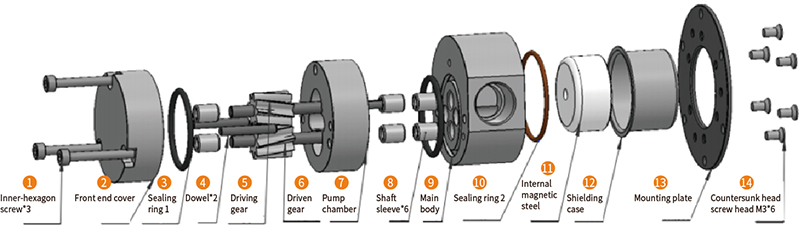
Why Choose CHENHUI?
Our high pressure micro gear pumps are desined for long-term reliability and performance, and we provide custom options with low minimum order quantities tailored to meet the needs of various industries. CHENHUI ensures that every pump is produced to meet the standard, providing efficient and cost-effective solutions for your business.
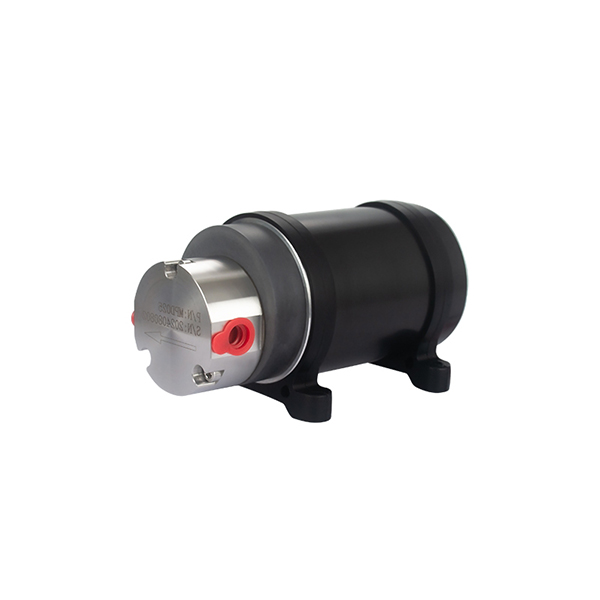
- Magnetic Coupling Technology
The pump is driven by a magnetic field instead of a direct mechanical shaft. This means there are no dynamic seals, so there’s no risk of leakage. It also reduces wear, making the pump last longer. - Long Service Life
Built with high-quality materials and precision machining, our pumps resist wear even under continuous use. This reduces downtime and maintaince costs over time. - Wide Temperature Range
Most models operate within a temperature range of -30°C to 120°C, with some models designed to handle temperatures from -10°C to 90°C. This flexibility makes their performance stay stable and reliable. - Easy System Integration
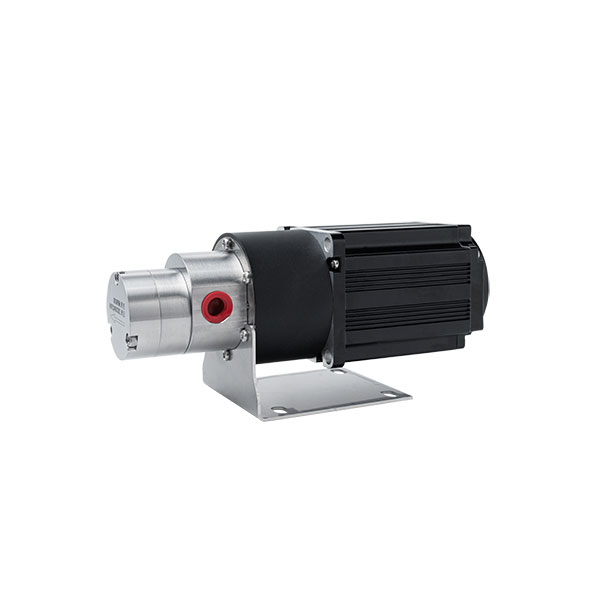
Our gear pumps feature a compact design and small size, allowing them to fit into tight spaces. They are easy to install when integrating into existing equipment.
FAQs
1. What is the Maximum Pressure for a Micro Gear Pump?
CHENHUI’s micro gear pump can handle a maximum system pressure of 40 bar. We also supply pumps designed for high differential pressure, up to 25 bar. Differential pressure is the key performance indicator for selecting the right gear pump. It shows how much resistance the pump can overcome when moving fluid through the system. A pump with higher differential pressure capability provides stable flow even under demanding conditions.
2. What is Differential Pressure in a Micro Gear Pump?
Differential pressure is the difference between the outlet pressure and the inlet pressure of the pump. It tells you how much pressure the pump creates to move the fluid through the system. If the pump sucks fluid in at low pressure and pushes it out at high pressure, that difference is the differential pressure.
3. How to Increase Pressure in a Micro Gear Pump?
-
Increase Pump Speed Carefully
Raising the pump’s speed can increase flow and pressure to some extent. However, pressure rise is limited by the system’s resistance and the pump’s mechanical design. Exceeding the recommended RPM risks damaging the pump and shortening its lifespan. Always follow manufacturer guidelines when adjusting speed. -
Set the Relief Valve Correctly
The relief valve acts as a safety device to prevent excessive pressure. Adjusting it properly ensures the system pressure does not exceed safe limits. While it does not directly increase pressure, correct relief valve settings help maintain stable system pressure and protect components. -
Use a Pump with a Higher Pressure Rating
The most reliable way to handle higher pressure requirements is to select a pump designed for greater pressure capabilities. Ensure all system components, including seals, pipes, and fittings, are rated for the increased pressure to maintain safety and performance.
4. What factors affect the pressure of a micro gear pump?
- Gear clearance — Smaller gaps reduce internal leakage, helping maintain higher pressure. But if the clearance is too tight, it increases wear and mechanical load.
- Drive speed — Higher speeds boost flow rate, but also cause pressure fluctuations. The maximum pressure is limited by the pump’s mechanical strength.
- System resistance and backpressure — The more resistance in pipes and valves, the higher the pressure the pump needs to work against. Exceeding design pressure risks damage.
- Sealing quality — Poor seals cause pressure loss, lowering effective output pressure.
- Temperature and fluid properties — High temperatures can reduce lubrication and sealing performance. Fluid viscosity affects how well pressure transfers.
- Materials and manufacturing precision — Better materials and tighter machining tolerances allow the pump to handle higher pressure with less leakage and wear.